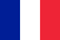
Psoriasis is one of the most common skin diseases; one in a hundred suffers from it.
Psoriasis is a disease for the development of which several factors are important at the same time: from hereditary predisposition (psoriasis in parents) to disorders of the functioning of the nervous system, endocrine, immune and other factors.
The reasons
The causes of psoriasis are not fully understood.
The principle of the mechanism of the disease is to disrupt the division of skin cells, which causes an autoimmune reaction (autoimmune reaction - occurs inside the body, does not depend on external threats).
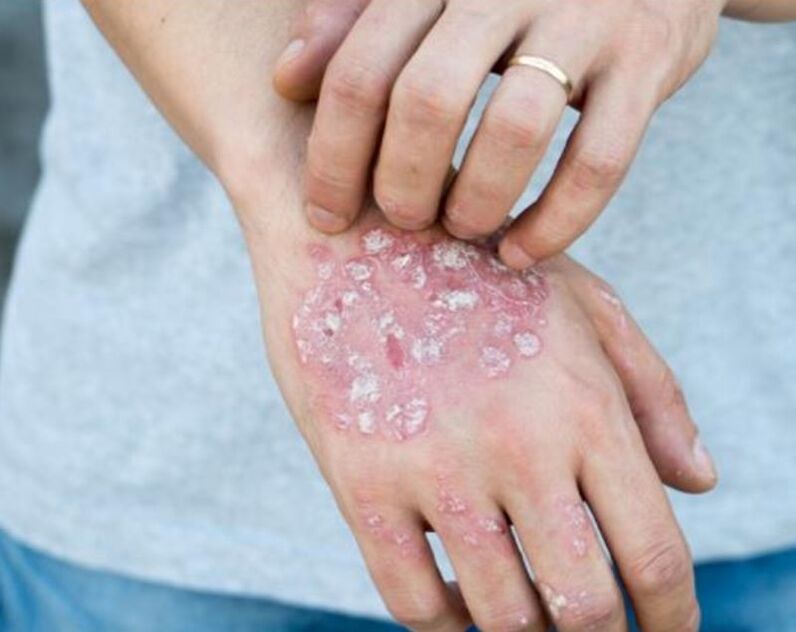
The top layer of the skin (epidermis) is mostly made up of keratinocytes - cells that produce keratin. Keratin is a protein, its properties ensure the protective function of the skin. Keratinocytes are formed in the deep layers of the epidermis and slowly move to its surface, during movement they mature and acquire new properties.
At the end of their "maturation", the keratinocytes form a horny layer on the surface of the skin. Then, the keratinized cells die and exfoliate from the living, so the life path of the keratinocytes comes to an end. This guarantees continuous skin renewal.
The normal journey of keratinocytes from the deep layer to the surface takes a month. With psoriasis, their lifespan is reduced to several days, which leads to the appearance of scaly psoriatic foci, since the skin does not have time to get rid of keratinized cells.
When they appear, psoriatic plaques are usually accompanied by itching and redness. This indicates an autoimmune reaction in the deep layers of the skin, resulting in swelling of the thick layer of the skin (dermis). The dermis contains blood and lymphatic vessels.
It is not known for sure why the process of keratinocyte formation is accelerated, but it is known that a hereditary factor has an important role.
The development of common psoriasis can begin due to:
- mental trauma and constant stressful conditions;
- damage to the skin;
- transferred infectious disease;
- take certain medications;
- hormonal disorders;
- allergic reactions (typical allergens: citrus fruits, eggs, chocolate);
- alcohol poisoning;
- climate change.
The psoriatic triad is a hallmark symptom of the condition that occurs when the skin is scratched.
Stearin stain(increased peeling after scratching, giving the surface of the papules a resemblance to a drop of crushed stearin).
Thermal film(the appearance after complete removal of scales from a wet, fine, shiny and translucent surface).
Point bleeding(the appearance of blood droplets not fusing with each other).
What happens to the skin in psoriasis?
In psoriasis, the structure of the skin is disturbed, the epidermis becomes thinner, the processes of keratinization of the skin (accumulation of keratin protein) are disturbed, and some layers of the normal epidermis disappear. In the next stage of the disease, clusters of cells responsible for inflammation are found in the protective superficial horny layer of the epidermis and in the zone of parakeratosis, around the dilated vessels of the skin.
Characteristic plaques and scales appear on the surface of the skin.
Psoriasis is not only a common disease, it has many manifestations and even disguises itself as other diseases.
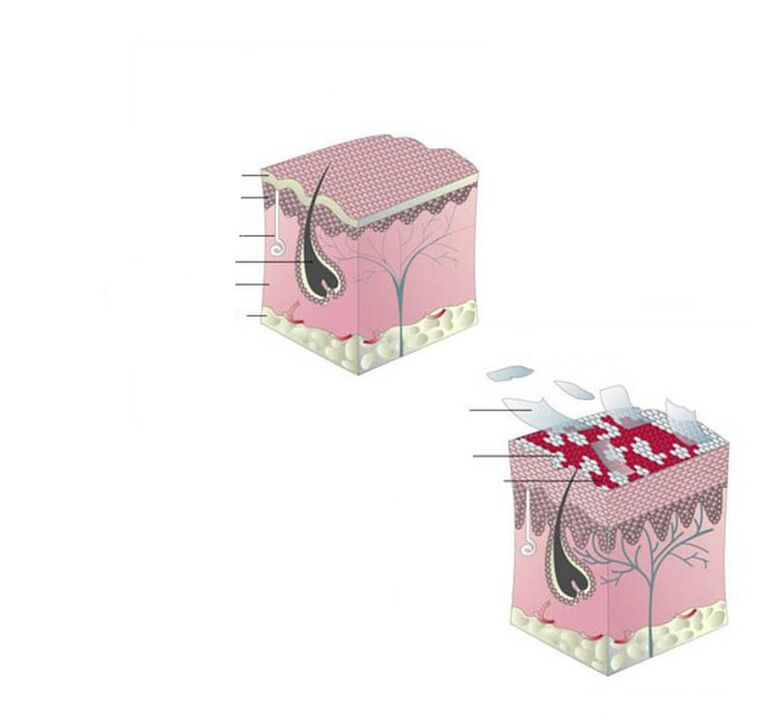
Psoriasis localization sites:
- elbows and knees;
- sacrum and kidney;
- scalp (seborrheic psoriasis);
- flexion surfaces and folds of the skin: the inner surface of the elbow and knee joints, the groin and armpits, the area under the breast (reverse psoriasis);
- palms and surfaces of the feet (palmoplantar psoriasis);
- psoriasis of the nail plates.
Common symptoms of psoriasis
The main symptoms of psoriasis are:
- psoriatic plaques;
- tightness of the affected skin area;
- itching.
Symptoms by type of psoriasis:
- exudative psoriasis (affected areas of the skin peel off and get wet, a yellow crust forms on the surface of the rash);
- intertriginous psoriasis (more common in children, the foci of occurrence are red, with slight scaling, sometimes wet can be confused with diaper rash);
- old psoriasis (it is characterized by large plaques that do not go away for a long time);
- rupioid psoriasis (another form of chronic psoriasis, characterized by a cone-shaped plaque);
- guttate psoriasis (a profuse rash of small papules).
Types of psoriasis
- Ordinary psoriasis (vulgar, plaque);
- Generalized psoriasis (widespread, postular);
- Teardrop-shaped psoriasis (depending on the type of rash);
- Arthropathic psoriasis (with joint damage);
- Other types of psoriasis (seborrheic and others).
Psoriasis vulgaris is the most common form of the disease.
Psoriasis begins with the appearance of rashes, often few in number, in typical places: on the elbows and knees. In addition, the characteristic localization of the rash is the area of the scalp and trunk. There is usually a clear link between the appearance of rashes and the action of the provoking factor.
Factors causing psoriasis can be stress, skin trauma, recent infectious disease, and regular alcohol consumption.
Usually, the exacerbation of the disease occurs in the cold season - this is the type of winter psoriasis. The summer type is rarer. Mixed forms of psoriasis are now noted. Over time, the number of rashes increases. They form characteristic psoriatic plaques. The Kebner phenomenon is observed - the appearance of new plaques in the places of skin trauma. Typically, patients have patches that remain on the skin even without exacerbation.
The disease circulates cyclically:
- Progressive stage (increased number of rashes);
- Stationary stage (new rashes do not appear);
- Regressive stage (regression of skin rashes, appearance in their place of skin areas without pigment).
Psoriasis vulgaris, photo
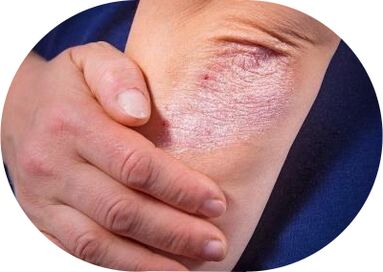
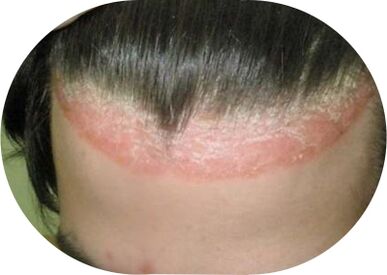
Diagnostic
When diagnosing psoriasis, first of all, a detailed examination of the skin is necessary.
Thin skin, bleeding in places, loose patches are signs of psoriasis. In the presence of these symptoms, the doctor performs a number of diagnostic measures to exclude the presence of other events with similar manifestations. For the final diagnosis, blood tests, smears and skin biopsies are done as needed. If the joints are affected, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is prescribed and x-rays are taken to identify the lesions.
Psoriasis vulgaris, treatment
Psoriasis is a systemic disease with skin manifestations, and complex treatment is required: both local and systemic treatment. The disease is chronic, and treatment is aimed at reducing the number and severity of exacerbations and achieving an acceptable skin condition for the patient.
At the progressive stage of psoriasis, all aggressive procedures are canceled: ultraviolet irradiation, baths. It is important that patients with psoriasis carefully and carefully handle the skin, do not injure it, in order to avoid exacerbation and the appearance of new plaques.
Diet for psoriasis
Psoriasis is often accompanied by liver disease, so it is important to avoid alcohol, fatty, fried and smoked foods. It is also important to be moderate in carbohydrate intake, as this changes the pH of the skin and increases the risk of infection of the rash.
Prophylaxis
Prevention of psoriasis is all about maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This helps prevent the onset of other diseases, as the body's immune system is protected from stress and can resist external threats.
Psoriasis prevention measures include:
- proper skin care;
- relaxing massage to improve blood circulation;
- good nutrition, it is advisable to avoid allergenic foods and to exclude (limit) the consumption of spicy, fatty, pickled, smoked, salty foods, as well as citrus fruits;
- dairy-vegetable diet;
- a sufficient amount of moisture in the body;
- elimination of alcohol and smoking and other bad habits;
- increased physical activity;
- outdoor walks;
- avoid stressful situations;
- take vitamins of groups A, B, C, D, E;
- choice of loose clothing made of natural materials that do not rub or cause irritation.
Means for the treatment of psoriasis
Systemic treatment of psoriasis aims to reduce the proliferation of the skin epithelium, stabilizing the keratinization of skin cells and cell membranes. For this, preparations based on vitamin A (retinoids), cytostatics are used. Among the most modern treatments, the so-called biologics are used, which neutralize the substances that cause inflammation.
For many years, UFOs have been used - treatment with ultraviolet rays of group B (in tanning beds, rays of group A), which reduce inflammation and contribute to the death of damaged cells. PUVA therapy involves the simultaneous use of ultraviolet rays and a special substance that increases the sensitivity of the skin to it.
An effective remedy for psoriasis
Local treatment is no less important than systemic treatment. It helps reduce skin inflammation. Medicines are prescribed depending on the stage of psoriasis.
Progressive stage
- exfoliating ointments and lotions;
- anti-inflammatory hormonal ointments with calcitriol;
- emollients to relieve itching and dry skin.
Stationary stage
- UVB therapy;
- concentrated exfoliating ointments;
- emollients to restore skin and reduce dryness.
Regressive stage
- concentrated exfoliating ointments;
- emollients to restore skin and reduce dryness.
Psoriasis cream
Creams and ointments for psoriasis serve different purposes and are used at different stages of the disease. Hormonal anti-inflammatory ointments and creams are used to stop inflammatory processes in the skin. There are several classes of hormonal drugs. They have different absorption capacities and different activities. When used in children, they try to avoid applying hormonal drugs to the face and neck, the area of skin folds - the places where the skin is thinner. Local preparations based on calcipotriol (a derivative of vitamin D) also have an anti-inflammatory effect. This is a later generation of drugs. They are currently not used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Salicylic ointment and salicylic acid lotion are designed to remove skin flakes with severe peeling. Salicylic acid not only has an exfoliating effect, but also increases the effectiveness of local hormonal drugs. In the stationary and regressive stage, when the inflammation has become less active, agents based on salicylic acid are used in a higher concentration.
Means for restoring the structure of the skin and eliminating dryness are used throughout the course of treatment, as well as in conjunction with ultraviolet irradiation to reduce itching of the skin. Once the breakouts have subsided, these products help maintain the protective properties of the skin and reduce the risk of new breakouts.
An effective cream against psoriasis
The modern approach to care and support for dry skin is based on saturating the epidermis with moisture and is called corneotherapy (derived from "corneo" - corneal or corneal layer of the epidermis).
Corneotherapy aims to restore the stratum corneum of the epidermis and its protective functions, which improves the condition of the skin as a whole. The work of the founder of corneotherapy Albert Kligman made it possible to create special means - emollients.
How do emollients work?
in the hour which follows the application of the emollients: - the condition of the skin improves, because the emollients "block" the humidity there.
6 hours after application of the emollients: - the structure of the skin is restored thanks to the content of special restorative natural lipids (ceramides and other useful fats).
24 hours after application of the emollients: - the clinical improvement of the skin condition is due to the penetration of moisturizing components into the deep layers of the epidermis and the restoration of the superficial layers of the skin (up to24 hours from the start of the application).